Day 4 / 100DaysOfWeb3
Today I will learn how to create and deploy my first smart contract with the web3 university simple tutorial.
For today's challenge I will be using the Ropsten test network using a Metamask, Solidity, Hardhat and Alchemy virtual wallet.
I use this tutorial on Web 3 University website.
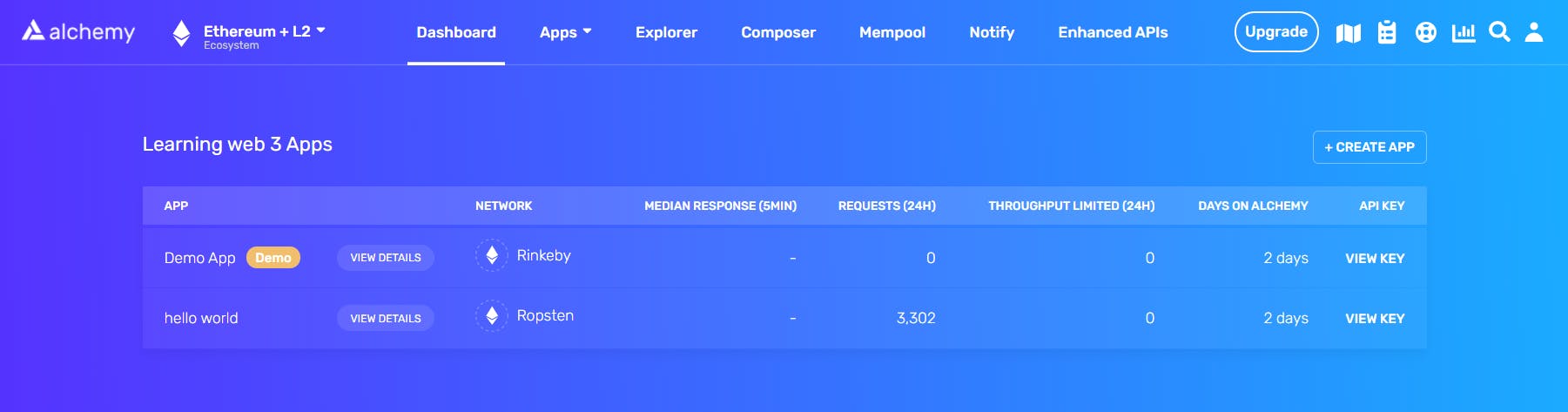
Step 1 : I created Alchemy account and created a new app named Hello world.
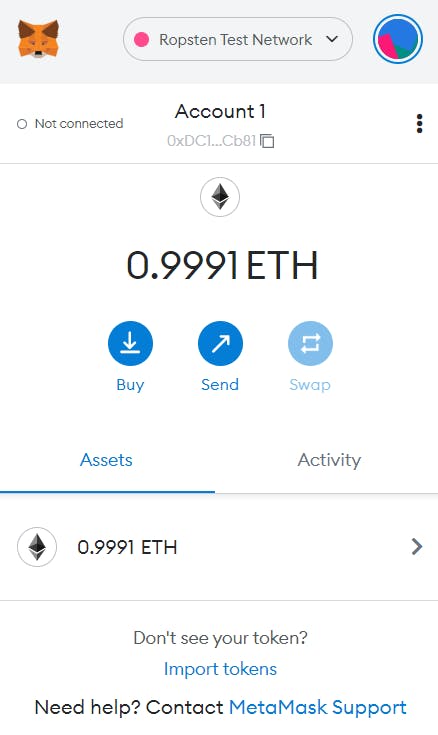
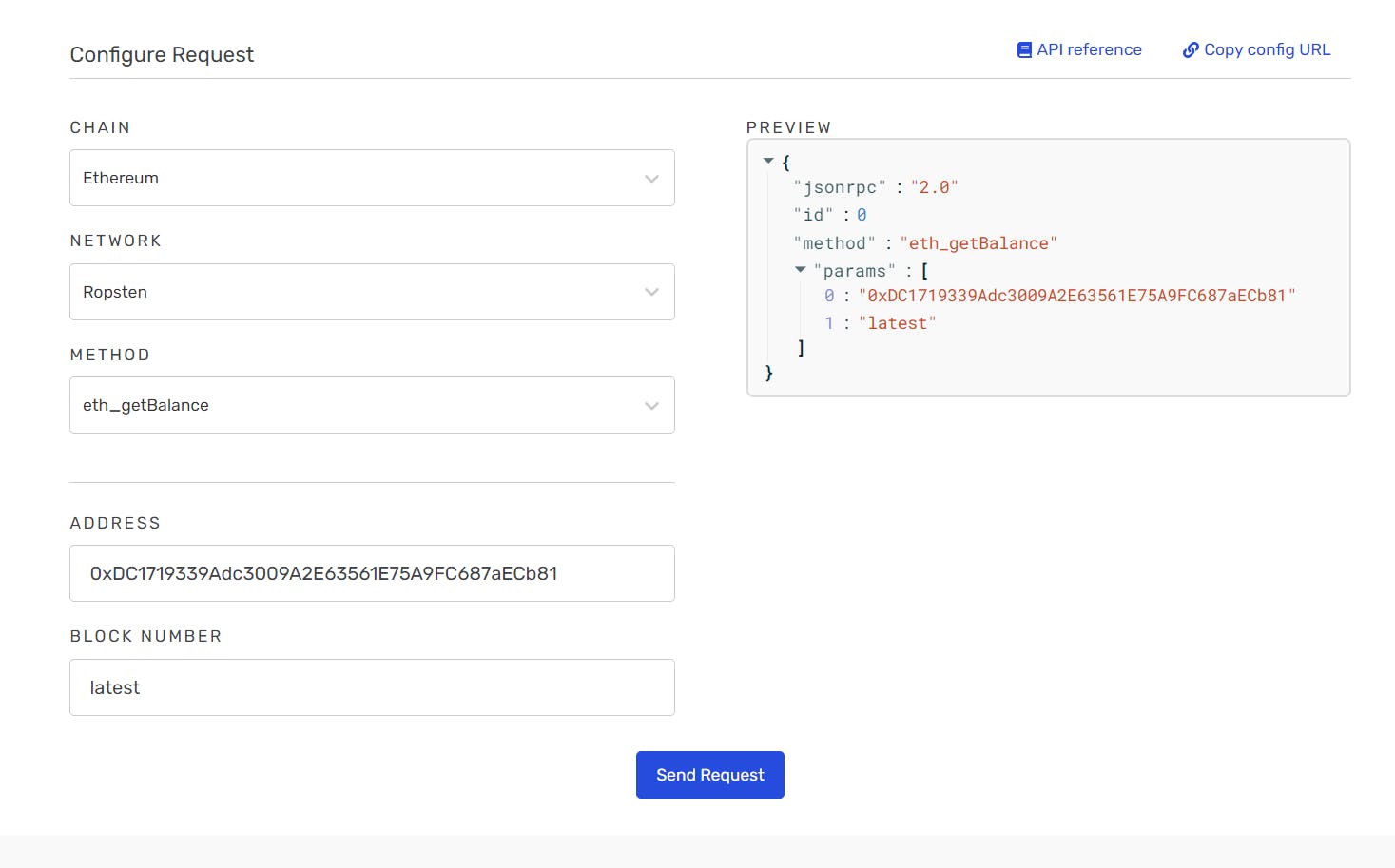
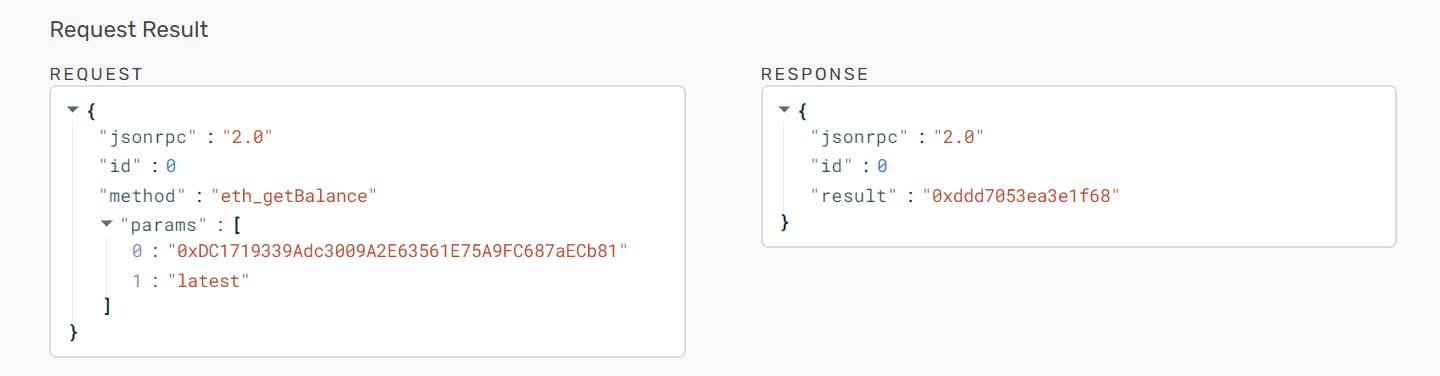
Step 2 : I created an Ethereum account and add ether from a Faucet through this link Ropsten faucet and check my account balance using Alchemy's composer tool
Step 3 : Create and Deploy project
- Initialize my project in a working directory with
npm init
- Add Hardhat to the project with
npm install --save-dev hardhat
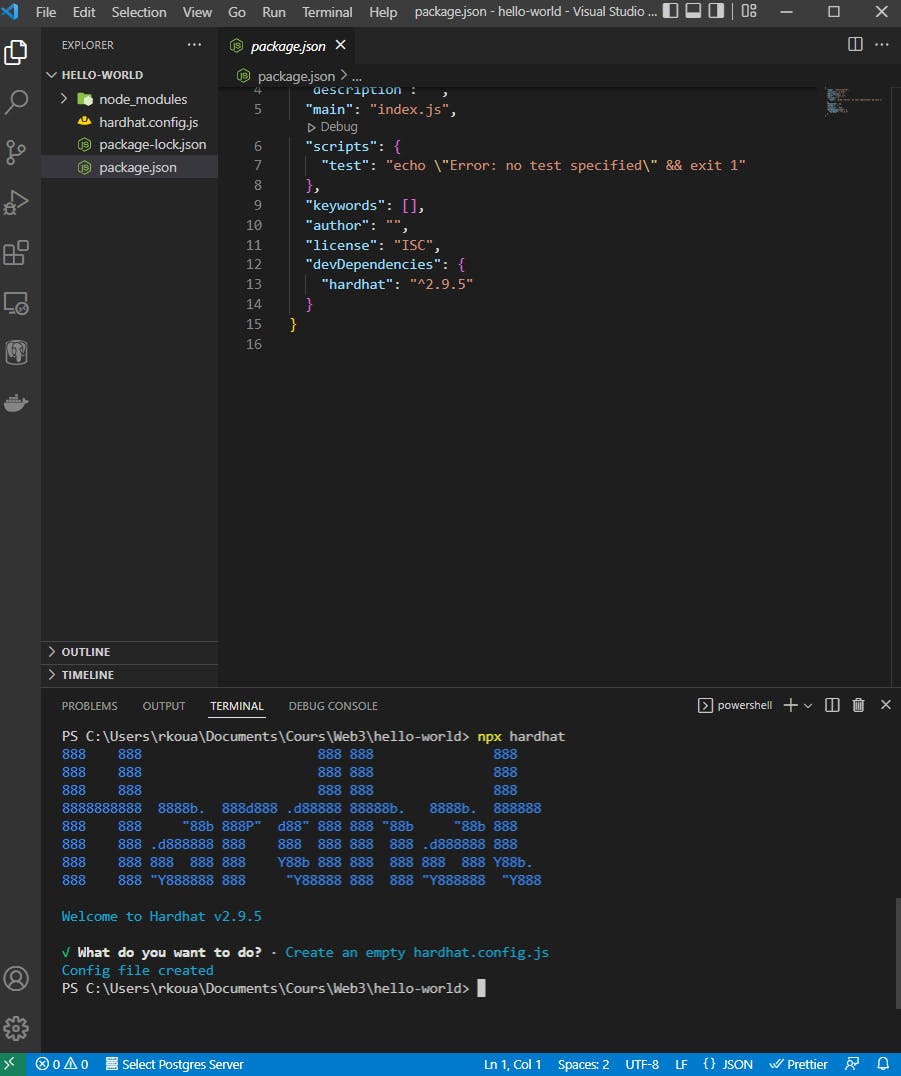
- Create hardhat project
npx hardhat
Add contracts and scripts directory to the project
I write my contract with this code
// Specifies the version of Solidity, using semantic versioning.
// Learn more: https://solidity.readthedocs.io/en/v0.5.10/layout-of-source-files.html#pragma
pragma solidity >=0.7.3;
// Defines a contract named `HelloWorld`.
// A contract is a collection of functions and data (its state). Once deployed, a contract resides at a specific address on the Ethereum blockchain. Learn more: https://solidity.readthedocs.io/en/v0.5.10/structure-of-a-contract.html
contract HelloWorld {
//Emitted when update function is called
//Smart contract events are a way for your contract to communicate that something happened on the blockchain to your app front-end, which can be 'listening' for certain events and take action when they happen.
event UpdatedMessages(string oldStr, string newStr);
// Declares a state variable `message` of type `string`.
// State variables are variables whose values are permanently stored in contract storage. The keyword `public` makes variables accessible from outside a contract and creates a function that other contracts or clients can call to access the value.
string public message;
// Similar to many class-based object-oriented languages, a constructor is a special function that is only executed upon contract creation.
// Constructors are used to initialize the contract's data. Learn more:https://solidity.readthedocs.io/en/v0.5.10/contracts.html#constructors
constructor(string memory initMessage) {
// Accepts a string argument `initMessage` and sets the value into the contract's `message` storage variable).
message = initMessage;
}
// A public function that accepts a string argument and updates the `message` storage variable.
function update(string memory newMessage) public {
string memory oldMsg = message;
message = newMessage;
emit UpdatedMessages(oldMsg, newMessage);
}
}
Step 4 : I connect MetaMask and Alchemy to my project by creating a dotenv file with these params
API_URL = "https://eth-ropsten.alchemyapi.io/v2/your-api-key"
PRIVATE_KEY = "your-metamask-private-key"
Step 5 : I Installed Ether.js with this code
npm install --save-dev @nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers "ethers@^5.0.0"
Then update hardhat.config.js to this :
/**
* @type import('hardhat/config').HardhatUserConfig
*/
require('dotenv').config();
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers");
const { API_URL, PRIVATE_KEY } = process.env;
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.7.3",
defaultNetwork: "ropsten",
networks: {
hardhat: {},
ropsten: {
url: API_URL,
accounts: [`0x${PRIVATE_KEY}`]
}
},
}
I compiled my contract with
npx hardhat compile
After compiled it, I create a deploy.js file in scripts folder
async function main() {
const HelloWorld = await ethers.getContractFactory("HelloWorld");
// Start deployment, returning a promise that resolves to a contract object
const hello_world = await HelloWorld.deploy("Hello World!");
console.log("Contract deployed to address:", hello_world.address);
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Step 6 : Deploy my contract
To deploy my contract, I run this command :
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network ropsten
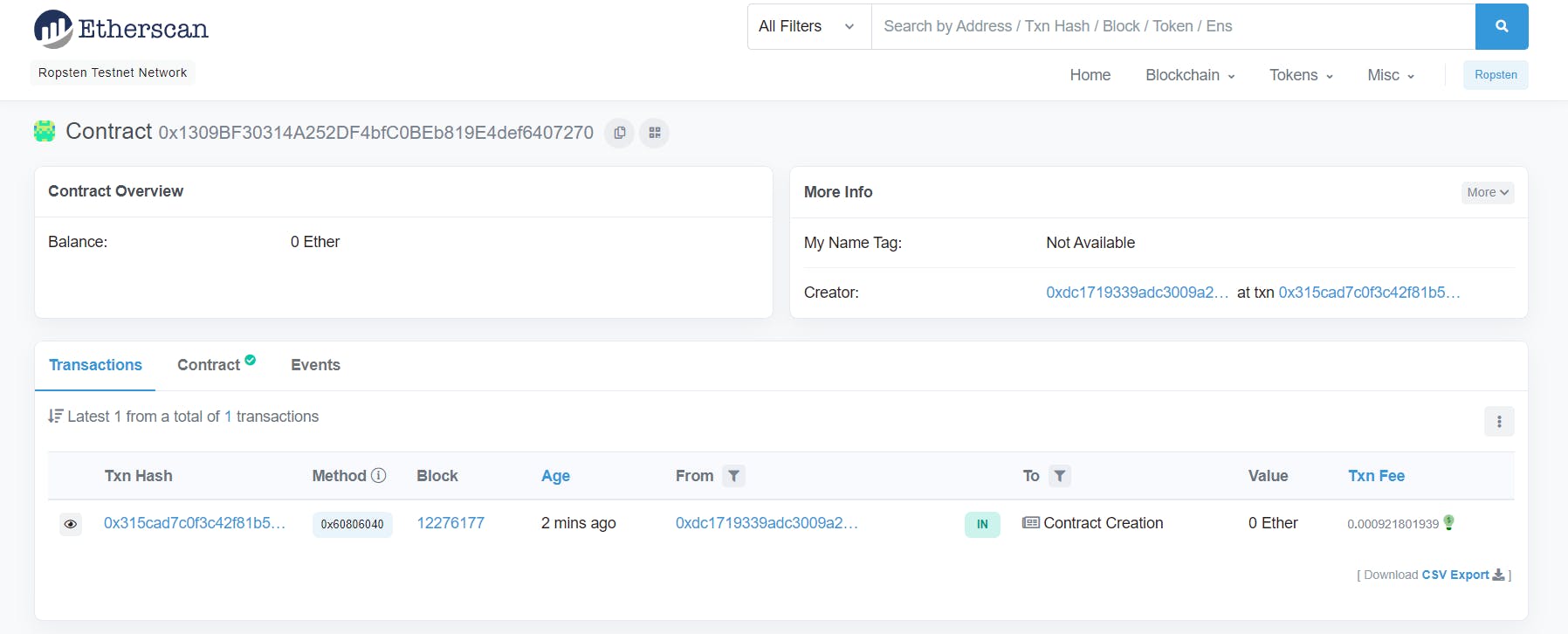
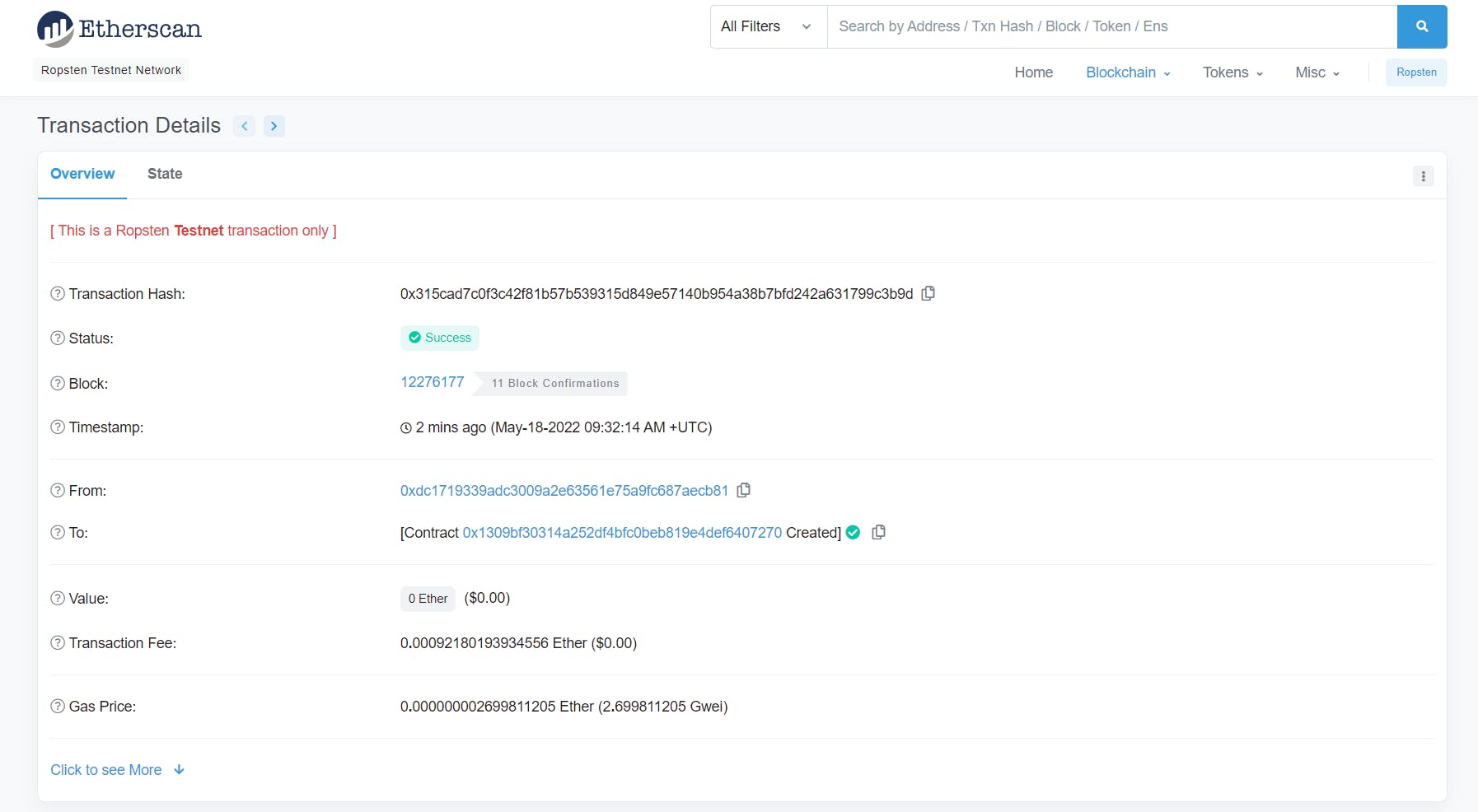
- My Contract is deployed to address: 0x1309BF30314A252DF4bfC0BEb819E4def6407270